Since ancient times, humans have looked skyward for their way. The ancient sailors used the constellations in the night sky as navigation. They were used to finding their position and destination. Today, we have a simple and portable GPS receiver that tells the current location of you and the distance from the destination, anywhere in the world. This is where GPS Satellites work on their purpose high in the sky.
Instead of stars, now we use satellites. These navigation satellites are used to tell the exact location on Earth. More than 30 navigation satellites hover above the Earth. Satellite navigation is based on a global network of satellites transmitting radio signals from medium-earth orbit. The users of satellite navigation are familiar with 31 Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites developed and operated by the United States.
What Is A GPS Satellite?
The Global Positioning System (GPS), also known as NAVSTAR GPS, is a satellite-based radio navigation system. It is owned by the government of the United States and under the operation of the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) providing the time and information and geolocation of the GPS receiver, anywhere on the Earth.
The GPS Satellite works well when there is a clear line of sight among the four or more satellites. It is because obstacles such as buildings or mountains can block the signal strength causing weak GPS signals. As a result, sometimes it gives inaccurate GPS location during hiking and hunting.
History of GPS Satellite
In 1955, Friedwardt Winterberg proposed a test of general relativity while detecting the slowing down of time in a strong gravitational field. It was due to the use of precise atomic clocks placed in orbit inside the artificial satellites. General and Special Relativity predict that observers on Earth would see GPS satellite clocks spinning 38 microseconds faster per day than clocks on Earth.
The design or introduction to GPS was proposed to eliminate the error of positioning which otherwise would calculate the position up to 10 kilometers per day of error. In 1973, the GPS project was initiated in the United States. It was to overcome the limitations of previous navigation systems. The idea was a combination of several predecessors while including the classified engineering design studies from the 1960s.
The U.S. Department of Defense deployed 24 satellites for military purposes. In the 1980s, GPS satellites were allowed for civilian use. The main credit of inventing the GPS satellites goes to:
- Roger L. from the Naval Research Laboratory
- Ivan A. Getting from the Aerospace Corporation
- Bradford Parkinson from the Applied Physics Laboratory
Gladys West’s work is considered fundamental in developing the computational techniques to detect the positions through satellites with the precision necessary for the GPS. The design of the GPS is based on similar terrestrial radio navigation systems such as Decca Navigator and LORAN, developed in the 1940s.
How Does GPS Satellite Work?
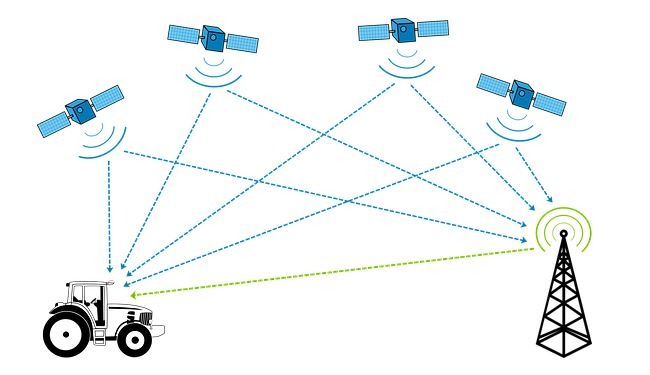
The basic GPS services provide the users with an accuracy of approximately 7 meters which is 95% accurate every time, anywhere on or near the Earth’s surface. For this purpose, each of the 31 satellites emits the signals that allow the receivers to use a combination of signals from at least four satellites. As a result, the precise location and time are determined from the combination of GPS satellites.
The time information is in the form of codes transmitted by the satellite. It helps the receiver to continuously determine the time at which the signal can be transmitted. The signal consists of the data received by the user to calculate the satellite locations and make adjustments necessary for the precise positioning.
Also, the difference between the time of signal reception and transmission is used by the receiver to calculate the range or distance between the satellite and receiver. The receiver must take into account propagation delays or reductions in signal speed caused by the troposphere and ionosphere.
When the signal was sent, the information about the ranges of three satellites and the location of the satellite, the receiver can calculate the three-dimensional position. A GPS-synchronized atomic clock is needed to calculate the distance of the three signals.
However, by measuring the fourth satellite, the receiver can avoid the need for an atomic clock. Hence, a receiver uses four satellites to calculate the time, altitude, longitude, and latitude such as GPS for bikes.
Mechanism And Components Of GPS
Space Segment
- Made up of satellites that transmit the signals from space based on the time and position of the users.
- The set of satellites is known as the constellation.
- A GPS uses two constellations of satellites such as GLONASS and NAVSTAR.
- NAVSTAR stands for Navigation Satellite Timing and Ranging.
- NAVSTAR is composed of 31 satellites in the orbit of 6 orbital planes, inclined 55 degrees relative to the equator, and a period of 12 hours.
- NAVSTAR orbits at an altitude of approximately 20,200 km each.
- Each satellite consists of four precise atomic clocks.
Control Segment
- Control Segment consists of a group of 5 ground monitoring stations, the main control station, and three antennas.
- The master control facility is located at Schriever Air Force Base, also known as Falcon AFB in Colorado.
- The monitoring stations continuously measure the signals of the SVs and provide the data to the master control station.
- The master control station calculates the satellite ephemeris and corrects the clock coefficients. Then it sends them to an antenna.
- The antenna transmits the data to each satellite once a day. The SVs then send subsets of the orbital ephemeris to GPS receivers via radio signals.
User Segment
- The GPS users segment consists of the GPS receivers and the user community.
- The receiver consists of a preamplifier and an antenna, a control and GPS display device, a radio signal microprocessor, a power supply, and a data recording unit.
- The SV signals are converted into the estimates of the position through GPS receivers. Minimum four satellites are required to calculate the four dimensions of the position such as X, Y, Z, and time.
Satellites by Block
Block | Launched | Operational | Testing/Reserve | Retired | Launch Failures | Manufacturer |
Block I | 11 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 1 | Rockwell International |
Block II | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | Rockwell International |
Block IIA | 19 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | Rockwell International |
Block IIR | 13 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 1 | Lockheed Martin |
Block IIRM | 8 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Lockheed Martin |
Block IIF | 12 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Boeing |
Block III | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Lockheed Martin |
Block IIIF | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Lockheed Martin |
GPS Satellite Services
GPS Satellites serve military and civilian users. The public services are accessible free of charge to all the users moving continuously around the world. For military purposes, GPS satellites are available to the United States and Allied armed forces and other government agencies.
Extensions
There are a variety of GPS augmentation systems and techniques available to improve the system performance and to meet specific user needs. They help to improve the integrity, accuracy, and availability of the signal while enabling better performance than possible with basic civilian GPS service.
Performance
Over many years, the excellent GPS performance has won the trust of millions of civilian users across the globe. Also, it has proven its reliability in the past and made promises for the benefit of users around the world shortly.
GPS Satellite – From Star Constellations To Satellite Constellations
Humans have been using various ways to find directions to their destinations. It started from star constellations when sailors and travelers used to depend on the directions by stars. They used them to know their current location and the distance and time from their destination. With advancements in GPS technology, the star constellations were replaced by satellite constellations. With a GPS Satellite, a person on or near the Earth’s surface can determine their precise location.
The working of a GPS satellite goes through the space segment, control segment, and user segment. Through radio signals and antennas, the GPS location of any person or equipment can be determined when connected to a power supply or internet connection. Usually, only four satellites are required to determine the GPS location anywhere on Earth, but more satellites can be used when signals are distorted due to obstacles in the way.